FACEBOOK NAVIGATION ICONS
Tuesday, 20 May 2014
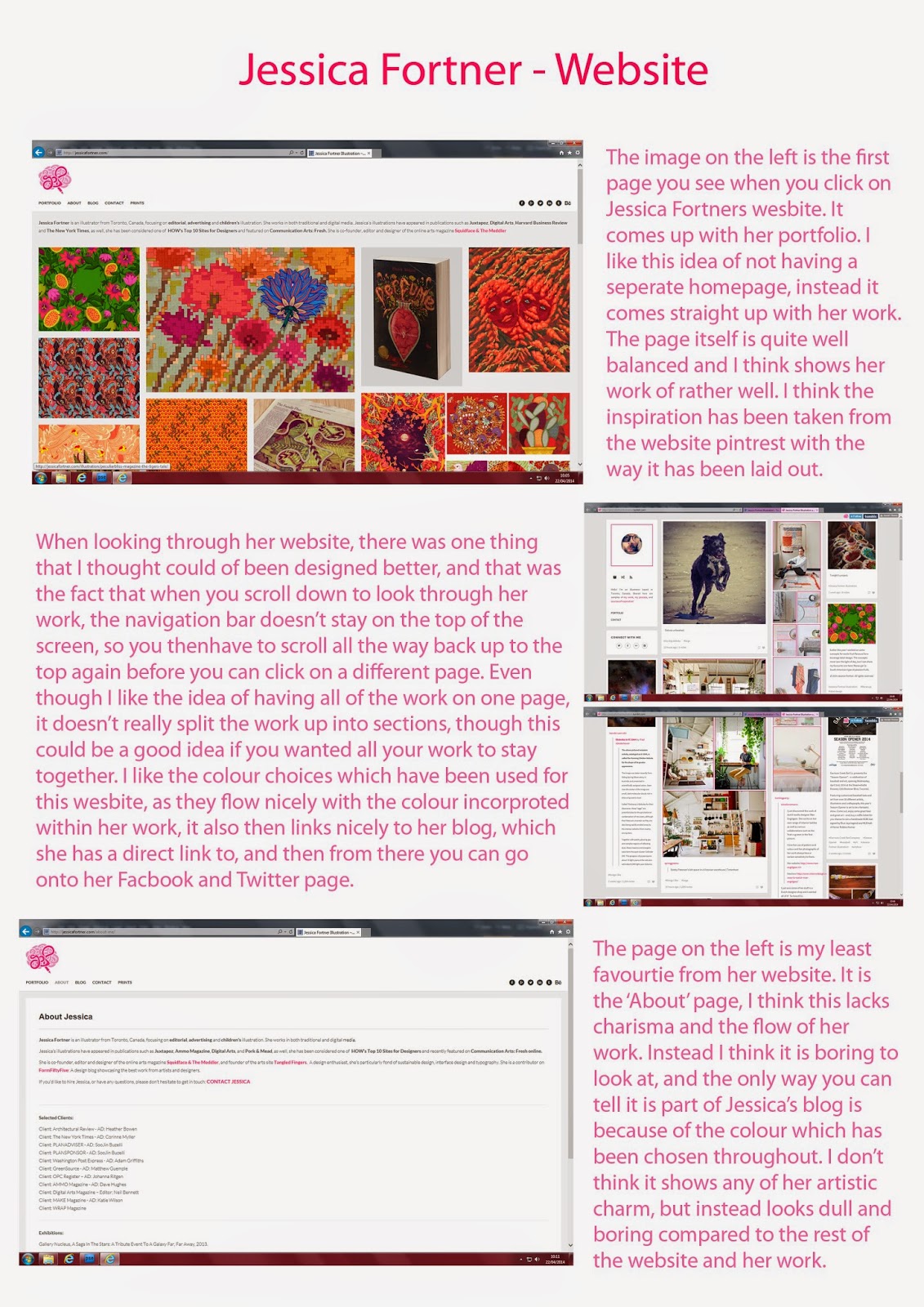
Website
Terms Glossary
Cookies:
Cookies
are small files which are stored on a user's computer. They are
designed to hold a modest amount of data specific to a particular
client and website, and can be accessed either by the web server or
the client computer. This allows the server to deliver a page
tailored to a particular user, or the page itself can contain some
script which is aware of the data in the cookie and so is able to
carry information from one visit to the website (or related site) to
the next.
Java:
Java is a programming
language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in
1995. There are lots of applications and websites that will not work
unless you have Java installed, and more are created every day. Java
is fast, secure, and reliable. From laptops to datacentres, game
consoles to scientific supercomputers, cell phones to the Internet.
JavaScript:
JavaScript is
a programming language used to make web pages interactive. It runs on
your visitor's computer and doesn't require constant downloads from
your website. JavaScript is often used to create polls and quizzes.
Perl:
Perl
is a programming language which can be used for a large variety of
tasks. A typical simple use of Perl would be for extracting
information from a text file and printing out a report or for
converting a text file into another form. But Perl provides a large
number of tools for quite complicated problems, including systems
programming. Programs written in Perl are called Perl
scripts,
whereas the term the
Perl program
refers to the system program named Perl for executing Perl scripts.
ASP
(Active Server Page): ASP
is also an abbreviation for application
service provider.
An Active Server Page (ASP) is an HTML
page that includes one or more scripts
(small embedded programs) that are processed on a Microsoft Web
server
before the page
is sent to the user. An ASP is somewhat similar to a server-side
include
or a common gateway interface (CGI)
application in that all involve programs that run on the server,
usually tailoring a page for the user.
Cascading Style
Sheets (CSS): CSS is an abbreviation for cascading style sheets;
it is used as a way to define the format and look/feel of the
website. This is important because you can separate the data from the
way the data looks, making the website easier to maintain, it also
makes the webpage easier to interpret for the web browsers by using
XML technology. The style sheets are called cascading as they are
separated into sections that can cascade or lay on top of each other.
HTML:
HyperText Markup Language
is the main markup
language for creating web
pages and other information
that can be displayed in a web
browser. HTML is written in
the form of HTML
elements consisting of tags
enclosed in angle
brackets (like <html>),
within the web page content. HTML tags most commonly come in pairs
like <h1>
and </h1>,
although some tags represent empty elements
and so are unpaired, for example <img>.
The first tag in a pair is the start tag,
and the second tag is the end tag
(they are also called opening tags
and closing tags). In
between these tags web designers can add text, further tags, comments
and other types of text-based content.
The
purpose of a web
browser is to read HTML
documents and compose them into visible or audible web pages. The
browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses the tags to
interpret the content of the page.HTML elements form the building
blocks of all websites.
HTML allows images
and objects to be embedded
and can be used to create interactive
forms.
XHTML:
Extensible HyperText Markup Language
is a family of XML
markup
languages that mirror or
extend versions of the widely used Hypertext
Markup Language (HTML), the
language in which web
pages are written. While
HTML (prior to HTML5)
was defined as an application of Standard
Generalized Markup Language
(SGML), a very flexible markup language framework, XHTML is an
application of XML,
a more restrictive subset of SGML. Because XHTML documents need to be
well-formed,
they can be parsed using standard XML parsers—unlike HTML, which
requires a lenient HTML-specific parser.
Dynamic
HTML: DHTML is an
umbrella term
for a collection of technologies used together to create interactive
and animated web
sites by using a
combination of a static markup
language (such as HTML),
a client-side
scripting language (such as
JavaScript),
a presentation definition language (such as CSS),
and the Document
Object Model. DHTML allows
scripting languages to change variables
in a web page's definition language, which in turn affects the look
and function of otherwise "static" HTML page content, after
the page has been fully loaded and during the viewing process. Thus
the dynamic characteristic of DHTML is the way it functions while a
page is viewed, not in its ability to generate a unique page with
each page load.
Uniform Resource
Locator ( URL ): A uniform resource locator, abbreviated as URL,
also known as web address, particularly when used with HTTP. A URL is
a specific character string that constitutes a reference to a
resource. In most web browsers, the URL of a web page is displayed on
the top inside an address bar. It cannot have spaces or certain other
characters and uses forward slashes to denote different directories.
Some examples of URLs are http://www.cnet.com/, http://web.mit.edu/,
and ftp://info.apple.com/. As you can see, not all URLs begin with
"http". The first part of a URL indicates what kind of
resource it is addressing. Here is a list of the different resource
prefixes.
Voice Over internet
Protocol ( VOIP ): A voice over internet protocol, abbreviated as
VOIP, is a technology that allows telephone calls to be made over
computer networks like the Internet. VoIP converts analogy voice
signals into digital data packets and supports real-time, two-way
transmission of conversations using Internet Protocol (IP).
Voice over internet
protocols calls can be made on the Internet using a VoIP service
provider and standard computer audio systems. Alternatively, some
service providers support VoIP through ordinary telephones that use
special adapters to connect to a home computer network. Many VoIP
implementations are based on the H.323 technology standard.
VoIP offers a
substantial cost savings over traditional long distance telephone
calls. The main disadvantage of VoIP is a greater potential for
dropped calls and degraded voice quality when the underlying network
links are under heavy load.
File Transfer
Protocol (FTP): FTP is a standard network protocol used to
transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP based
network, such as the internet.
Flash: Adobe
Flash is a multimedia and software platform used for authoring of
vector graphics, animation, games and rich internet applications
(RIAs) that can be viewed, played and executed in Adobe Flash Player.
FLV : Flash
Video (FLV) is a container file format used to deliver video over the
internet using Adobe Flash Player version 6 and newer.
SWF: An Adobe Flash
file used for multimedia, vector graphics and Action Script.
HCI: Human
computer Interaction (HCI) involves the study, planning, design and
uses of the interaction between users and computers. It is often
regarded as the intersection of computer science behaviour sciences,
design and several other fields of study.
Platforms: A
computing platform is,
in the most general sense, whatever pre-existing environment a piece
of software is designed to run within, obeying its constraints, and
making use of its facilities. Typical platforms include a hardware
architecture, an operating
system and runtime
libraries.
SWF PLAYER:
Swiff Player is a Free stand-alone player that enables Web Designers
and Flash Users to easily play their Flash movies. Swiff Player
offers a variety of playback capabilities including full-screen mode.
Shockwave Player:
Shockwave Player is the web standard for powerful multimedia
playback. The Shockwave Player allows you to view interactive web
content like games, business presentations, entertainment, and
advertisements from your web browser.
Audio Player: a
media player which can only play audio files.
JPEG:
"Joint Photographic Experts Group" or "Image file
format"
GIF: Graphics Interchange Format; GIFs are image files
that are compressed to reduce transfer time.
Animated GIF: A
type of GIF image that can be animated by combining several images
into a single GIF file
PNG:
Image file format
Advanced Content:
used to provide interactive menus and "special features"
such as additional bonus/extras content and games for HD
DVD (one of the high-definition
video formats). The Advanced Content runtime
engine is responsible for responding to user navigation input
e.g. JavaScript, Shockwave, image maps, slices, SWF, audio, videos,
Database; Conventions
World
Wide Web ; W3C: is
an international community where Member Organization, a full-time
staff and the public work together to develop Web Standards, led by
Web inventor Sir Tim Berners-Lee. The UK and Ireland Regional Office
is hosted by Nominet.
WCAG:
covers a wide range of
recommendations for making Web content more accessible. Following
these guidelines will make content accessible to a wider range of
people with disabilities, including blindness and low vision,
deafness and hearing loss, learning disabilities, cognitive
limitations, limited movement, speech disabilities, photosensitivity
and combinations of these. Following these guidelines will also often
make your Web content more usable to users in general.
IMAGE OPTIMIZING
GIF - Is good for icons and logos, something that is flat and simple with solid colours, this is because the maximum amount of colours in a GIF image is 256. Hasn't got great quality
JPEG - This is used for anything with a gradient, mostly photos are used in this format because of the amount of colours it holds, millions. Has really high quality.
PNG - This is Fireworks native image. It can have transparent, therefore able to have other shapes such as a circle, rather than just the standard square. This quality is inbetween GIF and JPEG.
PRINCIPLES OF WEB DESIGN
- Front End – What
you can see:
*Colour *Shape
*Texture *Composition
- Back End – How it
works:
*Links etc
*Programing *What makes it work
- Mock Up – Put a
design together visually:
*Photoshop
*Fireworks *72ppi – Resolution
- HTML – Hyper Text
Mark Up Language
*HTML 5 is the version
we are on now
- CSS – Cascading
Style Sheets
*CSS3 is the version we
are on now
- Java Script – Finds
different pictures and replaces them
- PHP, Pearl, C++ -
Allows websites to do things
- Servers – contains
information: For example movies
Website has to have
consistency and continuity:
For example headers or
homepage links
Accessible for disabled
people:
For example people who
are partially sighted or blind would need sound
Screen size has to be
adjustable:
For example screens
come in different sizes, computers, mobiles, tablets, TV's etcMobile apps are useful in this situation
- Adobe Kuler –
colour palette maker
-Hex (Hexdecimal) –
colour palette code – 6 numbers
When annotating sites
circle points you like or don't like, point out key features which
are obvious (little details)
- Hierarchy –
determines information, most important to least important.
This can be generated
through visual methods such as colour, composition, space, texture
and scale
-The fold – the line
at the bottom of the webpage
CONTRAST
People with poor eye sight would find it difficult if there was little contrast on a website, as nothing would be clear or would stand out.
This often has an impact on the hierarchy of the page.
Types
of contrast:
*Organic/Manmade
*Colour
*Texture/Flat
*Font/Images
*Scale – Big/Small
*Bright/Dark
*Messy/Clean
*Dull/Bright
*Curly/Straight
*Handmade/Computer generated
*Static/Movement
*Space – Crowded/Spacious
The top of the page is called the Header, this is normally where a
title, logo and navigation bar goes
The middle is called Content, this is where the bulk of your website
goes.
The bottom is called the Footer, this has little information and has
the least amount of contrast so it doesn't stand out.
BALANCE
Balance impacts the stability of a page.
Balance needs space.
There are two different kinds of balance:
*Symmetrical – this is mirrored, the same of both sides.*Asymmetrical – this doesn't really have a pattern, instead is the opposite of symmetrical
Symmetrical balance is achieved when the visual weight of each half
of a page is the same but not composed of similar elements.
The weight/balance isn't just effect by the size its also effected by
contrast.
- Gutter – Space between columns.
PROJECT PROPOSAL
For this project I will
be designing and creating a website to promote myself as a Graphics
Designer, as well as designing and creating a website for a chosen
client. I will be looking in to different web terminologies and
devising my own glossary to show that I have an understanding of the
abbreviations used in creating websites. I will be creating a
navigation bar and a sitemap, both of which will be used in my own
website design, to show that I have created my own parts of the
website from scratch. I will also be creating different style logos
for myself and a client and comparing which work best with the style
of the website, also I shall be creating navigation icons to place on
my website, for example for Facebook and Twitter, so my website can
be linked to social networking sites.
I will be looking into
and comparing the different software's used to create websites, and
finding out which I work best with, and therefore would use to create
my final design. I will be comparing the functions and features of
Wix, Moon-Fruit and Dream Weaver, but also trying out different free
website creators, to see if they are easier to use for an armature
website designer. I will also research other designers websites, to
find out where they got their inspiration from, and if there are any
design ideas which I could be inspired to use on my own website.
I will discuss the
drawbacks of designing a website, and how I would solve these if it
was me they would happen too. I will also be organising some studio
shoots, so I can use some new photos for either my clients website of
my selves, to show they variety of photography I use in my work. Also
I will be devising my own independent research, to either help
inspire the creation of my website design or help promote myself.
After creating my clients website and mine, I will take it through
the stages of analysis and review and refine the work, to see what I
could improve on, or what needs to be changed. I will then conduct a
survey to find out what other people think of my website, whether
they would visit it again, and what they would change about it. I
will then write up my findings in my final evaluation, and if I have
time I will take into consideration their views, and refine my
website even more.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)